The Scalability Issue
Blockchain always faces the trade-off issue between security and scalability. Though their PoW consensus protocol guarantees near perfect security, it also slows down the processing speed significantly. Currently, the Ethereum processing speed is 15 transactions per second while Bitcoin is 7 transactions per second. Both platform’s processing capacities are nowhere near Visa’s processing speed of 45,000 transactions per second. Furthermore, the increase in the number of
In seeking a viable solution to the scalability issue, Vitalik Buterin and Joseph Poon have joined hands in conceptualizing and developing Plasma, a framework that can scale Ethereum processing power. Joseph is also the co-founder of the Lightning network, a framework that has greatly increase Bitcoin processing speed. Both plasma and Lightning network are trustless multilayered blockchain networks.
Plasma
Plasma is a system that comprises the main blockchain and the ‘child blockchains’ that branch out from the main blockchain(aka parent blockchain or root blockchain). The child blockchains can co-exist but function independently from the parent chain and each other.
The Plasma system allows anyone to create their own child blockchains a.k.a plasma chains with their own smart contracts. Therefore, the Plasma system enables the creation of all kinds of use cases based on different business logic in their smart contracts. To ensure security, the root chain monitor and enforces the state in all the plasma chains and penalize the bad actors if there is proof of frauds. In this way, the Plasma system makes off-chain transactions possible while relying on the Ethereum main blockchain to maintain its security.
The Plasma Structure
Actually, the Plasma architecture is like a tree structure with the main Ethereum blockchain as the root. The child blockchains then branch out from the root blockchain, similar to branches grown out from the root of a tree. Every child chain, in turn, can spawn new child chains, the process can go on. Therefore, the plasma structure constitute a hierarchy of blockchains, as shown below:
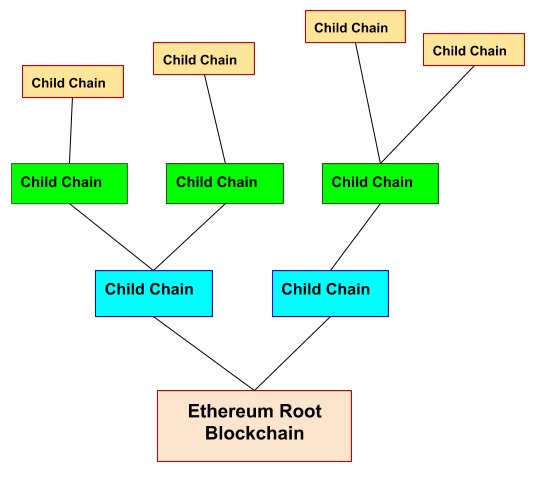
How does Plasma Works?
Plasma can greatly increase processing speed and throughput on the Ethereum blockchain because it allows off-chain transactions, similar to the payment channels of the Lightning network and other off-chain technologies. All the off-chain techniques take operations away from the main Ethereum blockchain.
State Channels
The concept of Plasma was derived from State Channels but improved on the latter. State channel works by creating an off-chain communication channel (a.k.a state channel )where transactions are not sent to the smart contract on the main chain, instead, they are sent through the Internet without touching the main blockchain. It is only after all the transactions have been completed (for example, a crypto game has finished) that the final state is sent to the smart contract on the main chain, closing the channel in the process. The smart contract will check the legitimacy of the transactions and release the asset (such as some ETH or a prize) to the recipient.
The state channel technique can improve scalability because it can reduce the number of transactions on the main blockchain. For example, a crypto chess game played between two players may involve hundreds of moves, which means hundreds of transactions will be executed on the Ethereum blockchain. However, if we use the state channel, we need to execute only 3 transactions that include registration of the players to initiate the game, submission of the final state to the blockchain and closing the channel.
Steps in Implementing Plasma
Plasma works in a similar way but with a different approach. Instead of creating the channels, it creates the child blockchains, as illustrated earlier. Smart contracts are created on the main Ethereum blockchain(The root chain) and they define the rules in the child blockchains. In other words, the smart contract serves as the root of the child blockchains. The child blockchains can employ their own consensus algorithm, such as proof of stake. The blocks validator will submit the state of the child chain to the Root Chain smart contract periodically. The smart contract will register the state of each Child Chain in the form of block hashes of the Child Chain.
We can illustrate how Plasma works by examining a crypto game such as
Plasma Exits
Plasma Exits is a security mechanism behind Plasma that allows users in a Plasma Chain to stop participating in the chain, and move their funds or assets back to the root chain. When a user wishes to exit a particular child chain, he or she needs to submit an exit application. The application is not immediately approved
Plasma is still evolving and now the Plasma team has come out with the improved version of Plasma known as Plasma cash. We shall discuss this new version in coming articles.
References

