The automotive supply chain is a highly complex and broad ecosystem with participants ranging from parts suppliers, manufacturers, sellers to aftermarket suppliers. All parts come with certain life expectancy, specific requirements and maintenance attributes. With thousands of spare parts, hundreds of parameters, and the number of manufactures distributed regionally or globally, the SCM team need to deal with a very large amount of data.
The two most common challenges are the need to keep inventories well-stocked but not overstocked, and the need to deal with the sheer amount of recalls. In addition, the industry is also facing a mirage of issues including tracking of parts, theft, counterfeit products, and data fraud.
Currently, centralized and siloed IT systems have been used to handle the issues but failed in many aspects. On the contrary, decentralized blockchain inherent features could offer perfect solutions to overcome the automotive parts supply chain issues.
- All participants share a common data
- Everyone has access to a single source of truth
- Reducing intermediaries
- Improved transparency
- Trust is embedded in the system
- Tamperproof due to its immutability
Blockchain technology can improve transparency across the supply chain and significantly reduces the cost and complexity of doing business with multiple parties. For automakers and suppliers, blockchain technology offers unique benefits starting with protecting their brands from counterfeit products to enhancing their brand experience by creating customer-centric business models.
Possible benefits of Blockchain usage in SCM
Identification and Tracking of Automotive Spare Parts
Counterfeit Protection -Verifying Authenticity and Origin
Counterfeit products are a significant issue for automotive manufacturers / suppliers and the counterfeit spare parts market is currently estimated at several billion dollars. Counterfeit spare parts are often of low quality and thus more likely to fail. This leads to dissatisfied customers and trust in the brand .
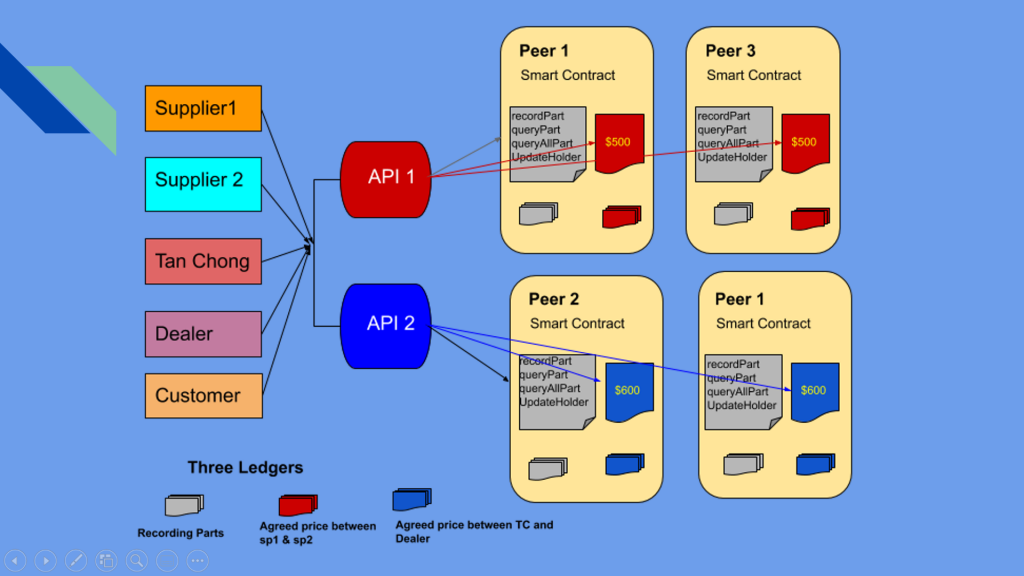
The Blockchain technology offers significant advantages over existing solutions where spare parts can be uniquely identified and digitally represented. The digital identification of these parts can be shared transparently to multiple parties in the blockchain business network.
Mutual collaboration is facilitated within the parties knowing that sensitive business information remains confidential. Confidentiality is enforced through blockchain cryptographic methods, hence protect integrity of the data not only from manipulators within the business network but also externally from attackers.
Spare parts service centers can accurately verify the authenticity of parts during replacement. The immutability of blockchain provides for a tamper-proof solution and offers a single source of truth. This will enhance the trust relationship between customers and the manufacturer.
Protection of Aftermarket Business
The global aftermarket business was valued at over 800 billion USD in 2018 and expected to grow to over a trillion USD over the next 10 years. Over 50% of this market consists of the sale of vehicle spare parts and business is split across OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and IAM (Independent Aftermarket) Suppliers.
As each product or part is uniquely represented on the blockchain, the technology can be applied to enforce business terms related to the exact production volume and timing. This level of enforcement can also be applied for manufacturers working with more than one supplier as part of their dual sourcing strategy.
Spare Parts Liability Resolution
In case a spare part needs to be replaced due to failure, liability needs to be established and this requires tracing the part back to the manufacturer. If parts are identified and digitally represented on the blockchain, it offers an accurate way to trace the origin. Liability is thus clearly established and is transparent to all parties in the blockchain. Any liability disputes can be resolved much faster and resources can be focused on customer engagement.
Vehicle Recall Optimization
Many of the recalls involve product defects that are life-threatening and automakers are exposed to a huge liability. With blockchain technology , the car and the individually assembled parts can be uniquely represented on the blockchain. If automakers can accurately identify which defective parts were installed in which cars, then the scope of the recall can be precisely executed thus result in massive cost savings.
Optimizing the Supply Chain Process
Inbound Logistics and Smart Manufacturing
Efficient planning of production capacity requires the manufacturing plant to coordinate between multitier suppliers, 3rd party logistics and transportation companies. Tracking and tracing individual parts across the inbound supply chain is complex and error-prone. Accurate, real-time information is not available and information is spread across individual databases.
By using a distributed immutable blockchain ledger across all parties, an accurate view of the status, quantity and location of the individual parts can be established. This can improve real-time logistics and plant production capacity.
Outbound Logistics Planning
The outbound supply chain in the automotive sector consists of a complex network of manufacturers, distributors, importers, and dealers. Like the inbound supply chain, participants in the outbound supply chain do not have a common data-sharing model.
Having a shared blockchain based system across the different participants will offer transparency and visibility. This will ensure faster transactions by lowering settlement periods.
Business Model Innovation
Car Personalization and Customer Engagement
The driver profile along with car customization preferences can be saved in a personal blockchain wallet. Shared or lease cars will authenticate the driver using the wallet and the car settings are personalized based on the driver profile. Automakers and mobility operators can thus create new business models focusing on individual preferences
Dynamic Pricing Models in Automotive Insurance and Leasing
A driver profile including miles covered, economical usage of vehicle and accident history is securely stored on the blockchain. Users share this data with providers offering insurance and leasing products based on their personal driving profile. The advantage that blockchain technology brings here is that the driver profile and historic events are immutably stored on the blockchain providing a single source of truth.
Digital Car Wallet
Ownership history, maintenance, and repairs can be transparently, and verifiably stored in a blockchain-based car wallet. Ownership record and fair price assessment of second-hand cars can be quickly established and transferring ownership can be done faster.
As vehicles are uniquely identified on the blockchain, stolen cars can be easily tracked and traced. Lack of trust and business friction arising in the transfer of ownership is hugely reduced. If repairs and parts replacements are verifiably tracked on the blockchain, warranty claims will be transparent for all parties.
M2M Transactions
Blockchain technology offers a unique way to automate transactions between machines and enable the future of M2M commerce. Cars in the future will be equipped with blockchain-based wallets and transactions with toll booths, park stations, and electric charging outlets will be automated without manual intervention.
The Solution-Hyperledger
Hyperledger is an open source effort created to advance cross-industry blockchain technologies hosted by The Linux Foundation. Hyperledger is a group of open source projects focused around cross-industry distributed ledger technologies. Hosted by The Linux Foundation, collaborators include industry leaders in technology, finance, banking, supply chain management, manufacturing, and IoT.
The Hyperledger project has been a collaboration of players from various industries and organizations in technology, finance, banking, supply chain management, manufacturing, IoT and more. Since its inception in December 2015, it has managed to enlist many prominent members that include IBM, Intel, NEC, Cisco, J.P Morgan, AMN AMRO, ANZ Bank, Wells Fargo, Accenture, SAP and more.
Hyperledger Fabric
Hyperledger Fabric is the first blockchain project developed and hosted by the Linux Foundation. According to the Linux Foundation , it was Intended as a foundation for developing DLT applications or solutions with a modular architecture.
Hyperledger Fabric is an open-source enterprise-grade permissioned distributed ledger technology (DLT) platform, designed for use in developing enterprise applications. It features some key differentiating capabilities over other popular distributed ledger or blockchain platforms.
Hyperledger Fabric is a blockchain framework that runs smart contracts called chaincode, which are written in Go. You can create a private network with Hyperledger Fabric, limiting the peers that can connect to and participate in the network. This private network can be hosted on AWS or other web service provider such as Microsoft Azure , Oracle or IBM.
One special feature of Hyperledger Fabric is that it allows components, such as consensus and membership services, to be plug-and-play. Besides that, Hyperledger Fabric uses container technology to host smart contracts called chaincode that comprises the application logic of the system.
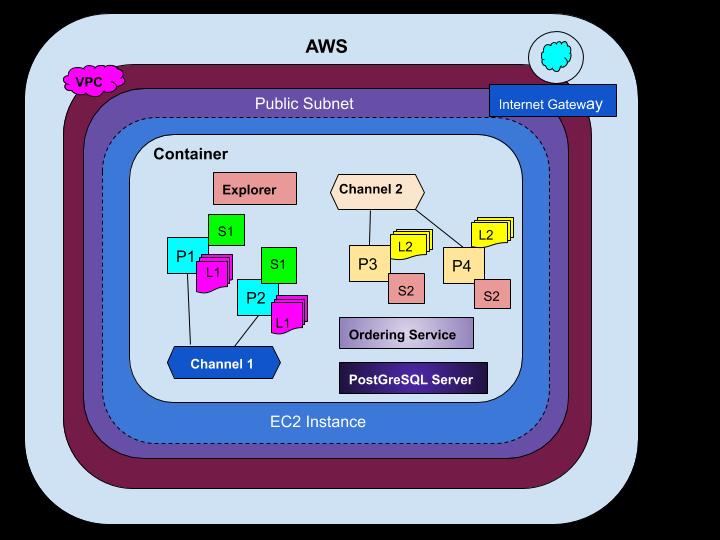
The AWS Blockchain Template for Hyperledger Fabric creates an EC2 instance with Docker and launches a Hyperledger Fabric network using containers on that instance.
The network includes one order service and three organizations, each with one peer service. The template also launches a Hyperledger Explorer container, which allows you to browse blockchain data. A PostgreSQL server container is launched to support Hyperledger Explorer.
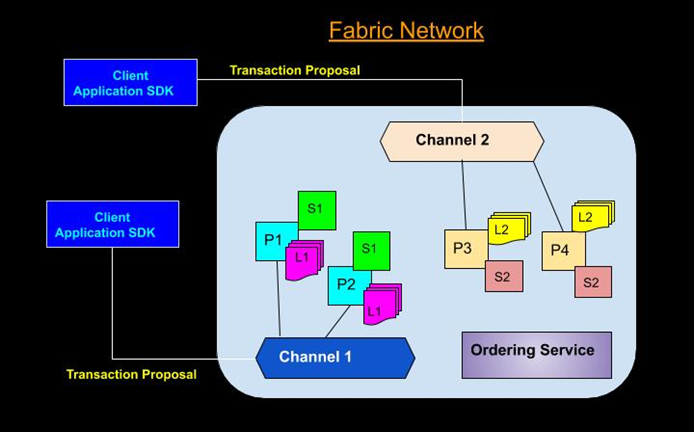
Channels are another unique feature of Hyperledger Fabric. They allow transactions to be private between two actors, while still being verified and committed to the blockchain.
Hyperledger Fabric Architecture
Hyperledger Fabric has a highly modular and configurable architecture. Therefore, enterprises can make use of its versatility to develop innovative business applications. Besides that, it can be used to optimize the applications. Indeed, Hyperledger Fabric is well suited to develop a broad range of industry use cases including banking, finance, insurance, healthcare, human resources, supply chain and even digital music delivery.
Hyperledger Fabric is a permissioned blockchain network that provides ledger services to application clients and administrators. It allows multiple organizations to collaborate as a consortium to form the network. The permissions to join the network are determined by a set of policies that are agreed to by the consortium when the network is configured.
Hyperledger Fabric Network
The Hyperledger Fabric network comprises the following components:
- Ledger
- Peers
- Ordering service Chaincode (aka smart contract)
- Channels
- Membership service provider
The Hyperledger ecosystem also consists of the client applications that allow users to interact with the network. Moreover, The Hyperledger Fabric application SDK provides a powerful API for developers to program applications to interact with the blockchain network on behalf of the users.
Channels are data partitioning mechanisms that allow transaction visibility for stakeholders only. Each channel is an independent chain of transaction blocks containing only transactions for that channel.
The chaincode (Smart Contracts) encapsulates both the asset definitions and the business logic (or transactions) for modifying those assets. Transaction invocations result in changes to the ledger.
The ledger contains the current world state of the network and a chain of transaction invocations. A shared, permissioned ledger is an append-only system of records and serves as a single source of truth.
The network is the collection of data processing peers that form a blockchain network. The network is responsible for maintaining a consistently replicated ledger.
The ordering service is a collection of nodes that orders transactions into a block. The world state reflects the current data about all the assets in the network. This data is stored in a database for efficient access. Currently, supported databases are LevelDB and CouchDB.
The membership service provider (MSP) manages identity and permissioned access for clients and peers.
Channels partition the Fabric network in such a way that only the stakeholders can view the transactions. In this way, organizations can utilize the same network while maintaining separation between multiple blockchains. The mechanism works by delegating transactions to different ledgers. Members of a channel can communicate and transact privately. Other members of the network cannot see the transactions on that channel.
References
- https://www.supplychainbrain.com/articles/29021-the-challenges-of-automotive-supply-chains
- https://medium.com/@jaymalaviya/smart-solution-for-supply-chain-challenges-in-automotive-industry-2d7e99dbbbe9
- https://www.inspirage.com/2016/07/supply-chain-challenges-automotive-industry/
- https://supplychainway.com/automotive-supply-chain-our-bread-and-butter/
- https://medium.com/coletiv-stories/blockchain-ready-supply-chain-management-system-using-hyperledger-composer-5970507e691f
- https://www.slideshare.net/rahulogy/automotive-supply-chain-managementa2z-by-rahul-guhathakurta
- https://www.fusioninformatics.com/blog/how-can-blockchain-benefit-the-automotive-industry/