The Building Block of ICP-Canister
Canister is a fundamental computational unit that combines both code and state. It is essentially a smart contract or a container that runs on the Internet Computer blockchain. Canisters are designed to be autonomous, scalable, and interoperable, enabling developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) and services.
Key Features of a Canister:
Code and State:
- Autonomous:
- Canisters operate independently and can interact with other canisters or external systems via messages.
- Scalable:
- The Internet Computer allows canisters to scale horizontally by distributing their workload across multiple nodes in the network.
- Interoperable:
- Canisters can communicate with each other through message passing, enabling complex decentralized applications to be built by composing multiple canisters.
- Upgradable:
- Developers can update the code of a canister without losing its state, making it easier to maintain and improve applications over time.
Cycle
n the Internet Computer (ICP), a Cycle is a computational unit used to pay for the execution of smart contracts (called canisters). It functions similarly to “gas” in Ethereum but is designed to be more predictable and cost-efficient.
Key Features of Cycles in ICP:
- Resource-Based Pricing – The cost of computation, storage, and network usage is measured in cycles.
- Stable Pricing Model – Unlike Ethereum’s gas, the cost of cycles is tied to real-world resources (compute and storage) rather than being market-driven.
- Conversion from ICP Tokens – ICP tokens can be converted into cycles to fund canister execution. The conversion rate is adjusted to maintain price stability. XDR (Special Drawing Rights) is used as a reference unit to determine the cost of converting ICP tokens to cycles in a stable manner.(1T Cycle = 1 XDR ~ USD1.321)
- Canister Management – Cycles are stored within canisters and consumed as operations are performed. When a canister runs out of cycles, it stops executing until refueled.
Cycle Usage in ICP:
- Computation – Each instruction executed by a canister consumes cycles.
- Storage – Data stored in the canister costs cycles over time.
- Inter-canister Calls – Messaging between canisters also consumes cycles.
- Network Operations – Data transmission to and from the Internet Computer incurs cycle costs.
Creation of a Cycle Wallet in Local Network
To create a cycle wallet in the local network, you start the local network in a clean mode using the following command:
dfx start –background –clean
Running the following command first time to create a cycle wallet automatically with 100T cycles in local network, otherwise it will return the cycle wallet id only.
dfx identity get-wallet
The following command will return the balance in the wallet:
dfx wallet balance
Motoko-The native programming language of ICP
Motoko is a programming language specifically designed for the Internet Computer (ICP) blockchain. It is optimized for writing smart contracts (called canisters) that run directly on the ICP network.
Key Features of Motoko
- Actor-Based Model – Uses the actor model to handle concurrency and asynchronous execution efficiently.
- Type-Safe & Memory-Safe – Strongly typed language that prevents common programming errors.
- Designed for Web3 – Integrates directly with the Internet Computer, supporting scalability, persistence, and seamless upgrades.
- Automatic Garbage Collection – Handles memory management internally.
- WebAssembly Compilation – Runs as WebAssembly (Wasm) for efficient execution on the ICP blockchain.
- Interoperability – Can interact with Rust, JavaScript, and other WebAssembly languages.
Create and Deploy Canisters
Creating a canister on the Internet Computer (ICP) involves a few simple steps. Below is a basic guide:
Start local network in background
dfx start –background
Create hello world project
dfx new hello
Select a backend language, you may choose Motoko, Rust, Python or Typescript, as shown below. We choose Motoko for our illustration.
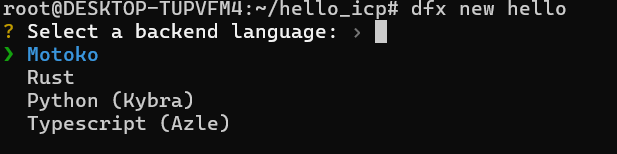
Then select a Frontend language as follows. We choose React for illustration.
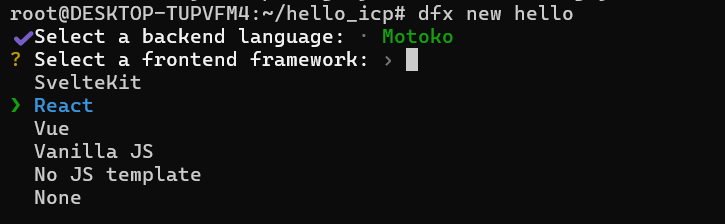
Then add extra features as follows, we choose Intenet Identity:
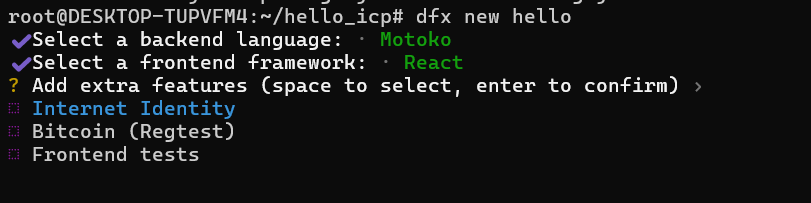
Pressing enter to confirm will create all necessary files and install dependencies, and arrive at the start up screen as shown below. A project with the folder name hello will be created.
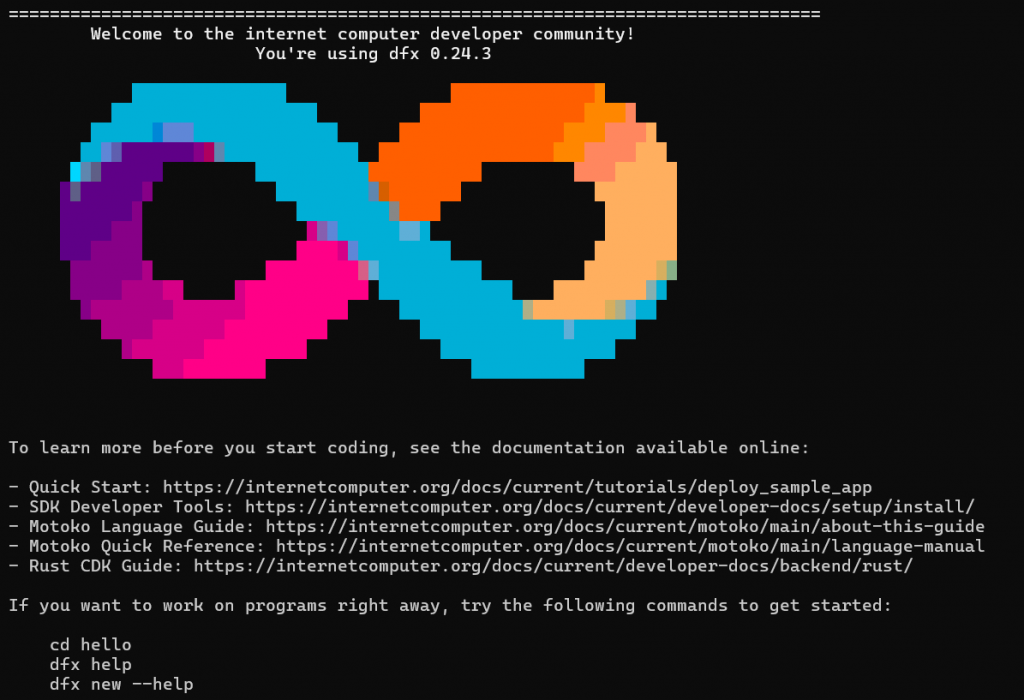
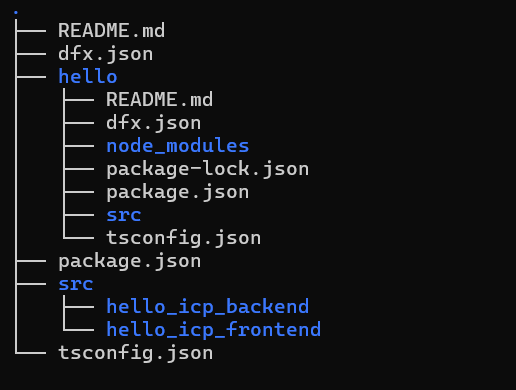
The project architecture is as shown below:
Deploying Canister on Local Network
To deploy the hello project you have just created on a local network, use the following command:
dfx deploy
The following screen shows successful deployment, otherwise there will be errors:
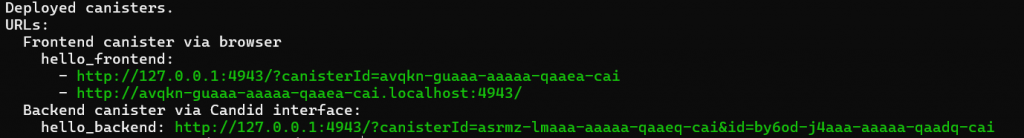
You may access the frontend URL via the link generated.
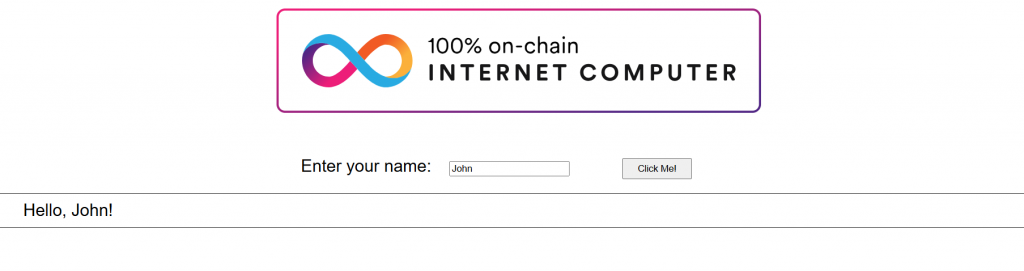
The frontend UI is as illustrated below:
Deploying Canister on the IC Mainnet
The command to deploy the canister on the IC mainnet is
dfx deploy –network ic
If the deployment on the IC blockchain is successful, the output will display the URLs of both the frontend and backend, as shown below:
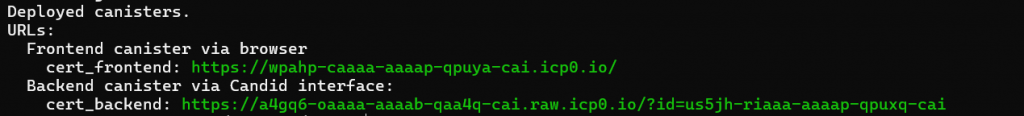
The frontend URL can be accessed on the desktop browser and the browser of the mobile devices. It does not need to register a domain nor a central server to host the web app, it is fully on chain.
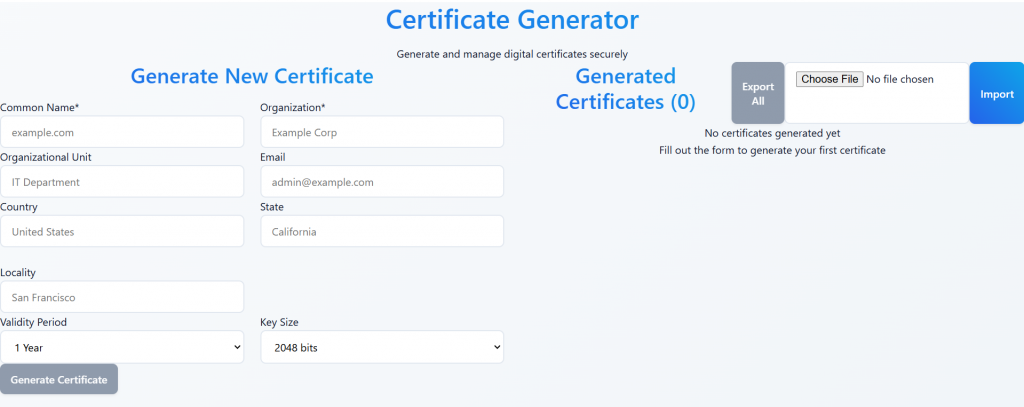
In this example, accessing the frontend URL with the link will display a certificate generator app, as shown below:
Obtaining Cycles
You need cycles to deploy your ICP app on the mainnet. There are two ways to obtain the cycles, one way is to redeem the coupon codes if you are given some free coupons, the other way is to buy icp tokens and convert them to cycles.
Method 1: Redeeming cycles from coupon codes
The command to redeem the cycles with coupon code is as follows:
dfx cycles redeem-faucet-coupon –network ic <COUPON_CODE>
Example: dfx cycles redeem-faucet-coupon –network ic CE3A9-BA578-CD44B
To check cycles balance in the wallet, use the following command:
dfx cycles –network ic balance
Method 2: Converting ICP tokens to cycles
First of all you must create an empty canister using ICP token using the following command:
dfx ledger –ic create-canister <principal-identifier> –amount <ICP tokens>
You may use the following command to obtain the principal identifier:
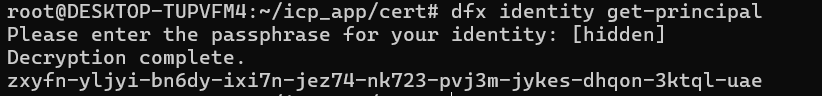
dfx identity get-principal
Example to get the principal identifier:
Then use the following command to convert ICP tokens to cycles:
dfx ledger –ic create-canister zxyfn-yljyi-bn6dy-ixi7n-jez74-nk723-pvj3m-jykes-dhqon-3ktql-uae –amount 0.3
To check canister status on the mainnet, use the following command:
dfx canister –network ic status <canister_id>
The status is as shown below:
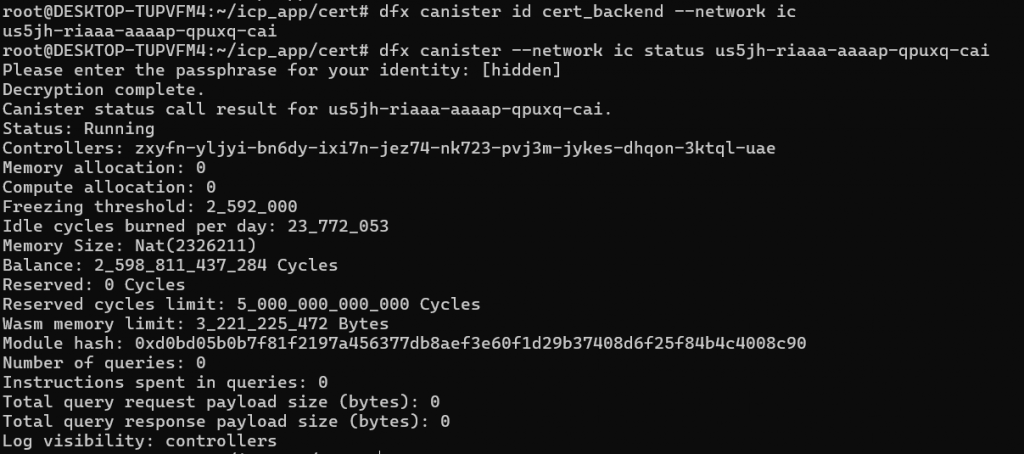
*You can obtain canister id on the ic mainnet using the command: dfx canister id <canister name>–network ic
Appendix: List of dfx commands
List all accounts in the device
dfx identity list
Show current identity
dfx identity whoami
Use a particular identity
dfx identity use <Identity Name>
Get ICP Tokens balance
dfx ledger balance
Top up cycles into cycle wallet or canister by converting ICP Tokens
dfx ledger –network ic top-up <wallet id or canister id> –amount <icp tokens>
Example: Add 4T cycles to your backend canister
dfx ledger top-up –network ic <canister_backend >–amount 4.0
Top up cycles directly
dfx canister –network ic deposit-cycles amount <canister_backend>
Example: Deposit 4T cycles to your backend canister
dfx canister –network ic deposit-cycles 4000000000000 weather_app_backend
To remove your identity in the device
dfx identity remove <identity name>
To get canister basic info
dfx canister –network ic info
To stop local network
dfx stop
To list the controllers of the canister:
dfx canister info ic_minter_backend

