The event management and ticketing industry is a huge market, particularly the event management software market. Markets Insider reported that the Event Management Software Market is projected to grow from USD 5.7 billion in 2019 to USD 11.4 billion by 2024, at a CAGR of 15% from 2019 to 2024.
However, despite the great potential of the event and ticketing industry, there are numerous problems and issues plaguing the current centralized event ticketing industry. The main issues include ticket counterfeiting, ticket scalpers, instant sell-outs and overpriced resale tickets on secondary markets (EventChain, 2017).
The good news is that the blockchain could fix the aforementioned issues. A blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that can be used to record transactions and other data across a decentralized peer-to-peer network made up of a cluster of computing devices.
Using blockchain technology, every ticket sales can be publicly verified, and thus the authenticity of the ticket can be guaranteed. It is also able to prevent fraudulent sales and counterfeiting. It sets rules (using smart contracts) preventing secondary ticket websites from hoarding tickets and charging inflated prices for premium events. If the rules are broken, the fraudulent accounts are frozen and the tickets are made invalid.
In a nutshell, blockchain-based event and ticketing system has the following benefits:
- Elimination of ticket duplication and counterfeit tickets
- Elimination of scalpers
- Elimination of ticket touts and purchasing bots
- Fully transparent ticketing aftermarket
- Automatic refund at the time of cancelation
Use Cases
BitTicket
The Edinburgh-based Citizen Ticket is an event ticketing platform backed by blockchain technology that uses the cryptocurrency Ethereum Classic. In May 2017, they deployed the blockchain-based ticketing system BitTicket and delivered the first live event using blockchain technology.
BitTicket is a ticket delivery service that event organisers, venues, and artists can use to secure their tickets with blockchain technology. BitTicket provides users with one wallet QR code that holds all their BitTickets securely, no matter which ticketing provider they bought them from. They simply present it along with proof of ID to gain entry. Due to the security of BitTicket identity, ticket transfer to friends and family can be done easily and with assurance. BitTickets are immutable, transferable, and verifiable.
BitTicket guarantees the following:
- Your purchased ticket is genuine
- Inherent protection against industrial-scale ticket touts and ticket purchasing bots
- Transfer your tickets securely and with ease between friends & family
- Provides one wallet for all your tickets – no more individual tickets
GUTS
GUTS uses blockchain technology to create a transparent ticketing ecosystem where inflated secondary market prices and ticket fraud are eliminated. Their motto is simple, transparent and secure.
GUTS brings numerous benefits for different stakeholders:
- Artist and Managers
- A fair chance for all the fans to attend the show
- Expand the fan base with exact data
- Direct communication with your fans. Send them a message right before the show starts.
- The venue, Festival and Theatre Operators
- No ticket fraud: fewer complaints and a stronger image
- You know exactly who is present, anytime (and who isn’t)
- Automatic refund procedure at the time of cancelation or resale
- Identification via mobile phones means a shorter queue
- Ticket Providers
- Complete control on the tickets at both the primary and secondary market
- Easy to integrate with existing ticketing solutions
LAVA
LAVA is a blockchain-based ticketing system that guarantees fair and secure smart tickets for music lovers. The system could prevent ticket touting and fraud ruining festivals for music lovers.
The LAVA ecosystem has the following features:
- 100% Safe
- Using latest blockchain technology to eliminate ticket fraud
- Smart Tickets
- Smart tickets to stop the exploitation of festival tickets using a unique digital footprint
- Lava Wallet-Eliminate printing completely by generating the ticket digitally and sending the digital ticket to the Lava wallet directly.
- No booking fee
PouchNATION
PouchNATION is an event management software system that uses the blockchain technology to good effect. PouchNATION is the first platform to implement blockchain and new digital currency across all verticals in event management. Its components comprise guest registration, cashless payment, access control, activity tracking, social engagement and detailed analytics reporting.
This innovative platform could overcome issues that the ticket industry is currently facing with managing events, attendance tracking apps, eliminating duplicate tickets, and validating registration at the door.
They have executed over 100 events including cashless events in Indonesia events in Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, Thailand, and Myanmar.
EventChain
EventChain is a global Smart Ticketing blockchain project that will allow events worldwide to sell SmartTickets through a peer-to-peer network, solving the issues of the centralized event ticketing industry.
It implements the EventChain token network for event management presents to ensure faster transactions, indisputable ticket vouchers, transparency from event hosts and fully flexible and programmable SmartTickets. With the use of the EVC token, smart contract code, and the Ethereum blockchain, EventChain’s transaction network brings increased accountability, transparency, and security to event ticketing.
To fix the excessive ticket fees, EventChain is distributing EVC tokens, a digital ERC20 token created for buying, selling, and programming SmartTickets on the Ethereum distributed network. EventChain claims that their transaction fees are much lower and the transaction confirmation speed is near seconds.
A Conceptualised Event Management and Ticketing Platform
After examining the above use cases, I propose that we can use a similar concept to develop blockchain-based event management and ticketing system for a decentralized platform. Below is a simple conceptual model of Event Management and Ticketing platform:
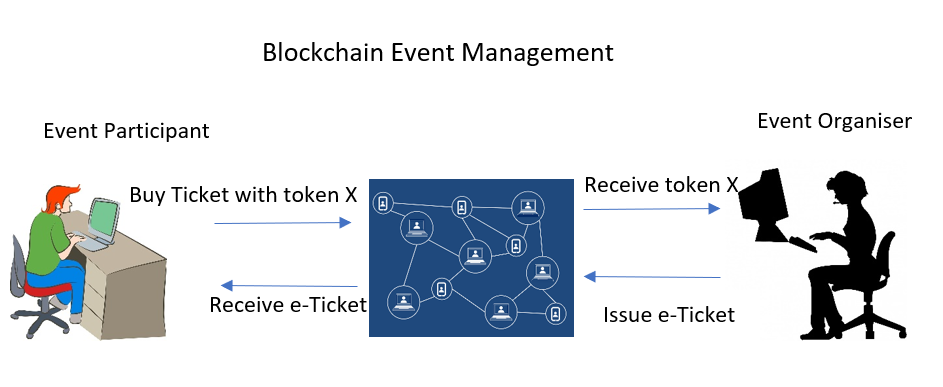
The platform allows an event organizer to create an event and broadcast it to the website as well as the Token X wallet. The event should comprise details such as event title, date, time, venue, and a ticketing ordering button. The participant can then order tickets by paying Token X. Once the organizer receives Token X, the e-ticket shall be automatically delivered to the participant’s mobile wallet. To enter the event venue, the organizer just needs to scan the e-ticket of the participant.
To build the platform, we need to build a smart contract layer on top of the platform to automate the buying and selling of event tickets. We shall use Solidity to write the contracts. There shall be at least two smart contracts – the event contract, and the ticket contract. The event contract will need to link to the ticket contract as it needs to use the data in the ticket contract. The keyword to access the data in another contract is import. For example, we can create an event contract event.sol that imports the ticket contract ticket.sol, using the syntax as follows:
Pragma Solidity ^0.5.0 import "./ticket.sol";
The event.sol file shall create an event contract that specifies event details such as total tickets, collected funds, start time, etc. The code could be as follows:
Contract Event {
struct EventDetails {
uint256 ticketAmount;
uint256 SoldticketAmount;
uint256 CollectedFunds;
uint256 StartTime;
}
The event contract shall also include a create event function, as follows:
function CreateEvent{
uint256 _ticketAmount;
uint256 _Startime
}
There are many more functions to be included in the smart contracts but I will not dwell further as this is not a technical paper.
References
- https://applicature.com/blog/blockchain-technology/smart-contracts-in-the-ticketing-industry
- https://www.corbinball.com/article/42-technology-how-to-use-it-better/224-blockchain-and-ethereum-how-can-they-be-used-for-events
- https://blocktix.io/
- https://www.citizenticket.co.uk/bitticket/
- https://www.bitticket.io/
- https://medium.com/coinmonks/how-blockchain-can-boost-the-ticket-booking-industry-79ea56fbfab
- https://guts.tickets/
- http://www.lavamovement.com/
- https://aventus.io/
- https://github.com/thek
- scar/Ticket-Sales
- https://github.com/qvissak/Ticket-Booth-Smart-Contract
- https://www.cryptoninjas.net/2018/08/28/event-management-dapp-blockparty-joins-status-blockchain-incubator/
- https://github.com/theNvN/event_management_dapp
- https://medium.com/evedo/blockchain-the-event-industry-e2c9e67c866e
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D9jO4kl9rTg&feature=youtu.be
- https://www.mci-group.com/news-and-insights/news/global/blockchain-top-uses-for-event-security-and-ticketing
- https://www.leadingedgeonly.com/blogs/how-blockchain-technology-is-changing-the-future-of-event-planning
- https://www.eventmanagerblog.com/blockchain-silver-bullet-attendee-experience
- https://www.slideshare.net/pouchnation/shaping-the-future-of-event-management-and-ticketing
- https://dex.openledger.io/what-benefits-can-blockchain-bring-to-the-event-management-business/
- https://blog.eventchain.io/eventchain-fixing-the-issues-of-the-event-ticketing-industry-d2f90f44d438
- https://medium.com/@andreazanda/blockchain-ticketing-a-disruptive-0-commission-ecosystem-e7cf45f38ec7
