In the previous post, you learned about the fundamental concepts of the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP), a third-generation blockchain designed to power the next evolution of the internet. At its core, ICP functions as a decentralized cloud, enabling developers to build and deploy applications entirely on-chain without relying on traditional centralized servers like AWS or Google Cloud.
You might be wondering—how is this even possible? To clear up any doubts, I will walk you through the process of creating and deploying an application on the Internet Computer. Unlike conventional web hosting, ICP allows you to launch apps without registering a domain name or provisioning a cloud server, leveraging blockchain-native web hosting for a truly decentralized experience.
Prerequisite
To start coding in IC(Internet Computer) , there are some prerequisites you need to set up or install before you can jump into developing your first app. Following are the prerequisites:
- Ensure you have the supporting operating system-
- Windows 10 or 11 with WSL2 installed with Ubuntu Linux v20.04
- Mac OSX 12 or above
- Ubuntu Linux v20.04
- NodeJs v20
- GitHub Account
- IC SDK
- Visual Studio Code IDE
- Basic programming knowledge- JavaScript, CSS, HTML
Here are the references to install the or set up the prerequisites:
- How to install Linux on Windows with WSL
- https://nodejs.org/en/download/current
- How to create a GitHub account
- Download VS Code
You must install IC SDK before you can start coding. Use the following command in the WSL ubuntu terminal to install the SDK:
·sh -ci “$(curl -fsSL https://internetcomputer.org/install.sh)”
After installation, check its version using the command dfx –version, you should see something like dfx 0.24.3
*·If you are using a machine running Apple silicon, you will need to have Rosetta installed. You can install Rosetta by running softwareupdate –install-rosetta in your terminal.
The next step is to create an account in IC. In ICP, authentication requires a key pair consisting of a private and a public key, while the account itself is identified by a unique principal ID. Additionally, a ledger is needed to store accounts and transactions. This ledger is a smart contract known as a system canister. Each user will have a ledger account identifier, also called an account ID, which is used to hold ICP tokens. Furthermore, a wallet must be created to store cycles and facilitate sending cycles to and from canisters.
Creating ICP Account
To create an account in IC, using the following command:
dfx identity new <identity_name>
·💡Identity names must use alphanumeric characters comprising uppercase and lower letters, numbers and special characters. Example: My_chatb@t
·ℹ️Most importantly, REMEMBER to back up the 24-word account/identity seed phrase. This is essential for restoring your account if you forget your password or need to access it from another device. Additionally, you can create multiple accounts on your device.
Principal ID
Having created your account, you can obtain your principal id using the following commands:
dfx identity use <identity_name>
dfx identity get-principal
Your account’s principal ID will resemble this:
zxyfn-yljyi-bn6dy-ixi7n-jez74-nk723-pvj3m-jykes-dhqon-3ktql-uae
Ledger Account ID
You can also obtain your ledger account id using the following commands:
dfx identity use <identity_name>
dfx ledger account-id
Your Ledger account ID will resemble this :
1370f0ea74b35f33d2a2fee64a7a8c53cd52d6dd82c1cdfe08712dcd863692ab
Importing Account
In case you have changed your device and need to use the same account to develop ICP apps, you may import the 24-word seed phrase you have saved as a plaintext into your new development environment using the following command:
dfx identity import –seed-file <seedfile.txt> <Identity Name>
ICP Token Balance
To check the ICP token balance in ledger account on ICP Main Network, use the following commend:
dfx ledger –network ic balance
·💡–network ic or –ic: Connect to ICP Main Network, without this parameter, it will connect to the local network
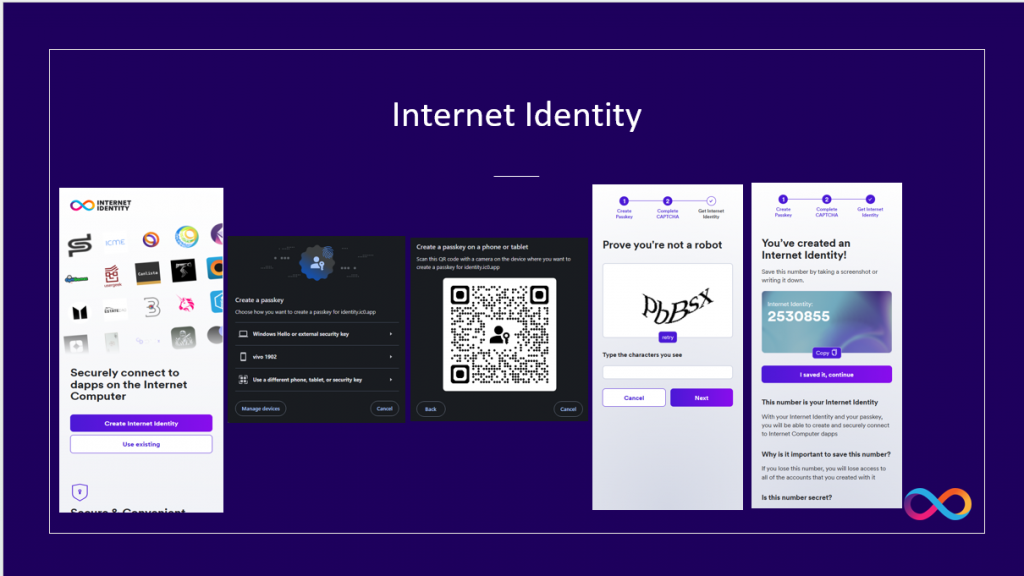
Internet Identity
Internet Identity is a decentralized authentication system for the ICP. If you haven’t already, set up an Internet Identity:
- Go to the Internet Identity portal: https://identity.ic0.app/.
- Click “Create New” to create a new identity.
- Follow the prompts to register your device . For Windows 10 user, require to use your mobile phone to scan the QR Code to store the credential information in the mobile phone. For Android device, recommend to use Google Lens to perform Passkey QR code scanning.
- Note down your Internet Identity number (e.g.,
12345).
ICP Account Address
To receive ICP tokens, you need an ICP account address associated with your Internet Identity. Here’s how to get it:
- Go to the Network Nervous System (NNS) Dapp: https://nns.ic0.app/.
- Authenticate using your Internet Identity.
- Once logged in, navigate to the “Accounts” section.
Plug Wallet
You may also use the Plug Wallet to store your ICP tokens. Plug wallet can be installed as a browser extension on a laptop or can be installed as a mobile app on your phone. You can download Plug Wallet using the link below.
Network Nervous System
The Network Nervous System (NNS) is the decentralized governance system aka DAO that controls and manages the Internet Computer (ICP), a blockchain-based computing platform developed by the DFINITY Foundation. The NNS is one of the most critical components of the Internet Computer, as it enables the network to operate autonomously and evolve over time through community participation.
Key Functions of the NNS
- Governance:
- The NNS allows ICP token holders to participate in the governance of the Internet Computer by submitting and voting on proposals.
- Proposals can cover a wide range of topics, such as upgrading the protocol, adjusting network parameters, or funding ecosystem projects.
- Token Economics:
- The NNS manages the ICP utility token, including its minting, burning, and distribution.
- It also handles the creation of cycles, which are used to pay for computation and storage on the Internet Computer.
- Node Management:
- The NNS oversees the addition, removal, and configuration of node machines that power the Internet Computer.
- It ensures the network remains secure, scalable, and efficient.
- Canister Management:
- The NNS manages the lifecycle of canisters (smart contracts) on the Internet Computer, including their creation, upgrading, and deletion.
- Network Upgrades:
- The NNS facilitates seamless upgrades to the Internet Computer protocol without requiring hard forks or downtime.
- This is achieved through a decentralized voting process.
